
High variety vs low variety conditions: vary the acts vs. Participants instructed to give 10 random acts of kindness over 10 weeks.
#Hedonic adaptation example series
Participants viewed a series of emotional target faces while in an fMRI machineĬonditions observe, affect label, gender label, affect match affect labeling resulted in the strongest reduction in amygdala activity Sheldon, Boehm, Lyubomirsky (2013) leads to insight about the vent affect labeling (def) putting feelings into words lieberman (2007) alters the way the event is represented in memory emotional inhibition is a long term low level stressor translating experiences into language.(4) -requires coherence, self reflection and multiple perspectives more positive outlook on life ((men benefit most)) emotional inhibition is. fewer physician visits in the next years Method: wrote about assigned topic 15 min per day for 4 daysĬonditions: emotional topic vs mundane topic PENNEBAKER (1989) (results) immediate: experimental subjects show distress make negative past experiences less surprising and variable by trying to understand and gain insight into them PENNEBAKER (1989) (hypothesis, method, conditions) hypothesis: giving people the opportunity to disclose emotions would improve health make recurring events as routine as possibleĢ. visualize it strategies for speeding adaptation to NA (2) 1. conditions: presence and absence (how it's impacted your life vs what your life would be like without it) comparing one's actual self to a hypothetical self who is worse off can make us feel better gratitude: maintaining freshness (3) 1.

asked to describe an event for which they felt grateful
#Hedonic adaptation example full
Within 6 months HEDONIC ADAPTATION had taken full effect Mental subtraction thinking about the absence of a positive event from one's life Koo 2008 Boyce, Brown & Moore (2010)Įach participants income ranked vs neighbors and ppl in similar fields life satisfaction more related to RANKED income than ABSOLUTE income Emmons & McCullough (2003) SET UP (3)Ĭonditions: five things you are grateful for, five hassles, anything grateful group: increase in life as a whole, upcoming week decrease in physical symptoms gratitude inhibits the impact of rising aspirations and upward comparisons that result from positive circumstantial changes Seligman (2005) gratitudeĪsked to write and deliver gratitude note to someone kind to them INCREASE in happiness, DECREASE in depressive symptoms even though they say they would be happier making more money but less than their colleagues.

social comparison relative, not absolute wealth (magazine example) people would choose to work at a place where they earn less money, but more than their colleagues. *we adapt less to changing and dynamic conditions factors drawing attention to NA (3) -positive-negative asymmetry
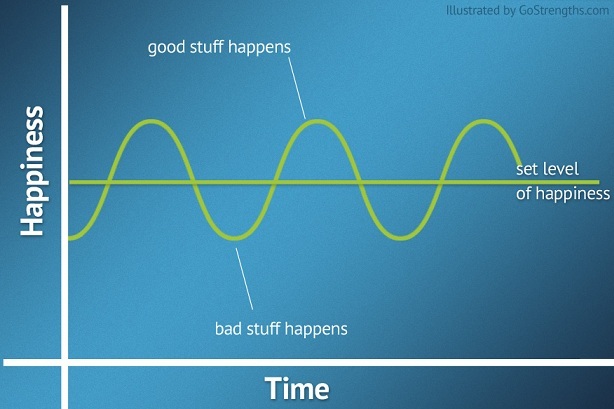
Speed of combatting hedonic adaption is affected by.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
